Published on September 4, 2024
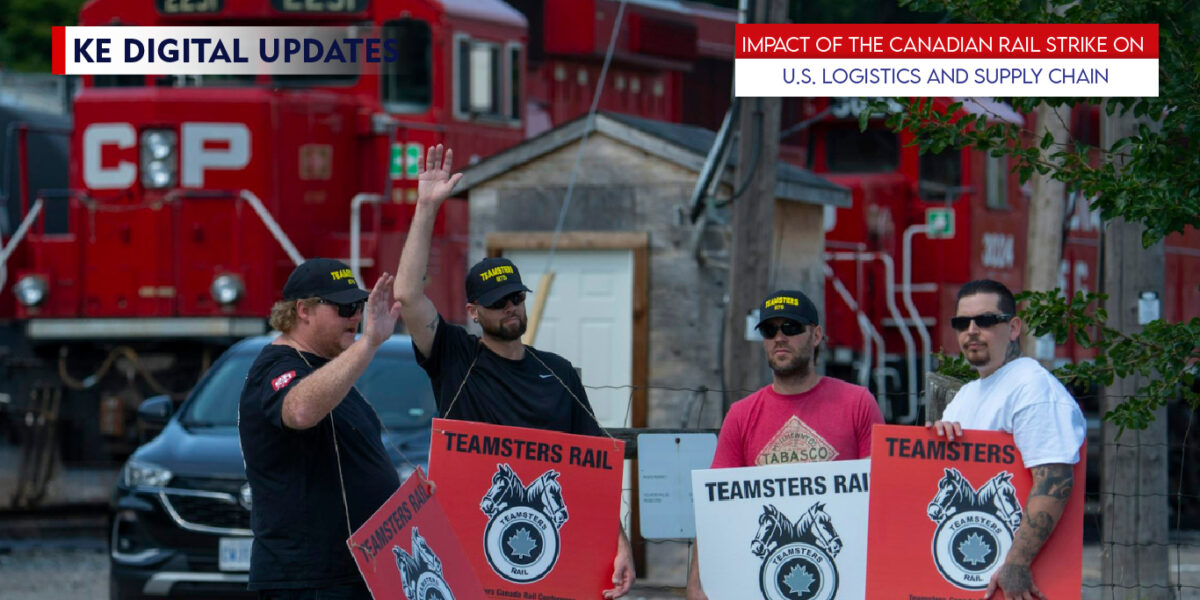
The recent rail strike in Canada has sent ripples through the logistics and supply chain sectors in the United States. The strike has led to significant disruptions as Canadian railroads are crucial in transporting raw materials and finished products across North America. Here’s a detailed look at the various implications:
1. Increased Shipping Costs
With rail services disrupted, many companies have had to turn to alternative transportation methods, primarily trucking. Trucking, however, is generally more expensive than rail transport. This shift has led to increased shipping costs for businesses, which may eventually be passed on to consumers through higher prices for goods.
2. Delivery Delays
The sudden need to switch from rail to truck transport has caused delays in delivery times. Railroads can move large quantities of goods efficiently over long distances, and the loss of this capacity has strained the logistics network. Companies are experiencing longer lead times, which can disrupt production schedules and inventory management.
3. Tighter Shipping Capacity
The increased demand for trucking and other alternative transportation methods has led to tighter shipping capacity. Fewer trucks and drivers are available to meet the heightened demand, further exacerbating delays and increasing costs.
4. Sector-Specific Impacts
Different sectors are feeling the impact of the rail strike in various ways:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on railroads to transport bulk commodities like grain and fertilizer. The strike has delayed shipments, potentially affecting planting and harvesting schedules.
- Automotive: The automotive industry depends on timely deliveries of parts and materials. Disruptions can halt production lines, leading to significant financial losses.
- Energy: Railroads are essential for transporting oil, gas, and coal. Delays in these shipments can affect energy production and distribution.
5. Long-Term Trade Agreements
The strike has also highlighted vulnerabilities in long-term trade agreements. Companies that rely on predictable and reliable transportation for their supply chains may need to reassess their logistics strategies and consider diversifying their transportation options to mitigate future risks.
6. Broader Economic Implications
The disruptions caused by the rail strike extend beyond individual companies and sectors. The overall economy can be affected as supply chain inefficiencies lead to higher costs and reduced availability of goods. This can contribute to inflationary pressures and impact economic growth.
Conclusion The Canadian rail strike has underscored the interconnectedness of North American supply chains and the critical role that railroads play in maintaining efficient logistics operations. As companies navigate the challenges posed by the strike, they may need to explore alternative strategies and build more resilient supply chains to withstand future disruptions.